Science and Technology Class 14
A BRIEF OVERVIEW OF THE PREVIOUS CLASS AND Q&A SESSION (05:07 PM)
CHALLENGES WITH AI (05:24 PM)
- AI systems can be biased if they are trained on biased data or designed with biases. This can lead to discriminatory outcomes. In fact, AI can learn biases from the data itself. Example- An bot designed by Microsoft learned all the conspiracy theories in 6 hours and after that, it started promoting those conspiracy theories.
- Transparency and accountability issues- If an AI commits a mistake, who should be held accountable? For example- Tesla cars caused the accident.
- AI relies on a heavy amount of data. It is important to ensure that data privacy is maintained.
- Emergence of AI tools threatens a lot of jobs such as data entry jobs, customer service, and support jobs, accounting jobs, and even basic levels of coding jobs.
- AI can have negative applications such as the use of deep fakes for fake images and videos.
- India-specific challenges- For developing countries such as India there are challenges associated with Skills and infrastructure to develop AI tools. [* limited availability of skilled workforce, lack of cloud computing infrastructure, data security, and privacy issues]
- ESSAY TOPIC- Artificial Intelligence: challenges and Opportunities (125 marks/ 1000-1200 words)
DATA PROTECTION REGIME (05:48 PM)
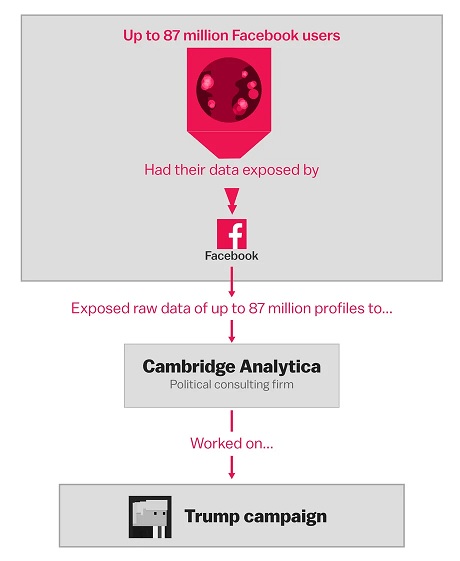
- Case study of Cambridge Analytica- Violation of personal data during elections. Personalized Advertisements were sent to the persons on whom they are sensitive.
-
- Data protection regime
- It refers to practices, technologies, and regulations to safeguard sensitive information of individuals from unauthorized access, disclosure, or use. It empowers citizens regarding their private data and holds data collection entities accountable for their practices.
- European Union took the lead and came up with 7 principles known as General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR). These principles include
- a) Lawfulness, fairness, and transparency- organizations need to ensure their data collection practices don't break the law and that they are not hiding anything from the data subjects.
- b) Purpose limitation- Organizations should collect personal data for a specific purpose, clearly state what that purpose is, and only collect data for as long as necessary to complete that purpose
- c) Data minimization- Organisations must only process the personal data that they need to achieve its processing purposes.
- d) Data Accuracy- Every reasonable step must be taken to erase or rectify data that is inaccurate or incomplete
- [* Data accuracy and Data minimization together give the Right to be forgotten. Right to be forgotten means it is the right of the person to ask the entity to delete the personal data ]
- e) Integrity and confidentiality- Data must be processed in a manner that ensures appropriate security against accidental laws, destruction or damage, and unauthorized or unlawful processing.
- f) Accountability- Organizations will be fined if they do not adhere to the above 6 principles
DATA LOCALISATION and DATA COLONIALISM (06:12 PM)
- The term data localization refers to the practice that data collected within a country must be stored, processed, and used within that country's borders.
- Data colonialism- It refers to the exploitation of data resources of one group or country by another group of countries often without their consent.
- Homework- Digital data protection Bill 2023- Read the features
- [* Follow this link- https://prsindia.org/billtrack/draft-the-digital-personal-data-protection-bill-2022]
- [* Pegasus- It is a type of malicious software or malware classified as spyware. It is designed to gain access to devices, without the knowledge of users, gathers personal information, and relays it back to whoever it is that is using the software to spy]
DEFENSE TECHNOLOGY (06:46 PM)
- Framework
- Missiles
- Ships and Submarines
- Airpower
- Emerging trends in warfare
- Indigenization of technology
- Indigenisation denotes to substituting an imported item with one that is manufactured within the country.
- In the Pharma sector, India is the main exporter. But still, the main ingredient required to give therapeutic effects to medicine i.e. API (Active pharmaceutical ingredients) are imported from China.
- India is also the largest buyer of defense equipment [India and Saudi Arabia occupying the top position]- Report of SIPRI (Stockholm International Peace Research Institute)
- Why indigenization of defense has not occurred?
- Defence expenditure is very less. Allocation in the budget is less. And even in the less allocation, the R&D gets very less.
- Most of the expenditure goes to the salary and pension and very less goes to R&D.
- Skillforce required is lacking.
- Private sector participation is very less. The product developed by the private sector is rejected by the public sector company. [* Case study- Israel, France, USA- Private sector has more participation, and their democratic credentials are not threatened ]
- Too much regulation, lack of startups, Bureaucratic red-tapism.
- Lack of Availability of raw materials.
- Many defense deals have resulted in opaqueness, and many corruption news/scandals were evident.
- Nexus between the private contractors- the government resulted in corruption.
- Proper national security doctrine is still not there.
- Achievement so far
- Brahmos are demanded by the Philippines, and Armenia ordered Pinaka missiles.
- Defense corridor is coming up in two states- Tamilnadu and Uttar Pradesh.
- FDI is coming into the defense sector.
MISSILE TECHNOLOGY (07:03 PM)
- Missile is a rocket-propelled weapon that carries a warhead and delivers it with great accuracy at high speed.
-
- There can be various types of missiles based on different criteria
- A. Based on the launch platform and target
- 1) Surface to Surface- Agnii series of missiles
- 2) Surface to Air- Akash missile
- 3) Air to Air/ Air to surface- Astra missile
- 4) Anti-tank missiles- Nag, and Helina.
- B. Based on speed
- Mach no.- Speed of object/Speed of sound. The speed of sound is 330-340 m/s at NTP(normal temperature and pressure)]
- 1) Subsonic [Speed less than Mach 1],
- 2) Transsonic [Mach 1]
- 3) Supersonic [1-5 Mach],
- 4) Hypersonic [More than Mach 5]
- C. Based on the range-
- 1) Short-range missiles (less than 1000 Km),
- 2) Medium-range missiles (1000-3000 Km),
- 3) Intermediate-range missiles(3000-5000 Km),
- 4) Long-range missiles (More than 5000 Km.) Long-range missiles are also called Inter-continental ballistic Missiles [ICBMs].
- D. Based on Trajectory-
- 1) Ballistic missiles, and
- 2) Cruise missiles.
-
- Ballistic missiles-
- These missiles follow a ballistic trajectory with the objective of delivering warheads to a pre-determined target. They are guided for a brief duration in starting phase and the rest of the path is like a free-falling projectile under Earth's gravitational force.
- Often these missiles cross the atmosphere and re-enter it. They can hit a target very far away and consume less fuel because of this we can also increase the mass of warheads.
- They can have a longer range with less consumption of Fuel, For example- Agni and Prithvi.
- Challenge- However, they are suitable for stationary targets and can be intercepted by Radars early into the flight
- [* Radars- They emit radio waves. And they intercept the reflected waves. These reflected waves are monitored. They can intercept the Ballistic missile and they can be neutralized. ]
- Cruise missiles-
- It is a guided missile that remains in the atmosphere and does not change its altitude and speed significantly.
- These missiles are often self-navigating and because they fly at low altitudes, they can avoid interception by radars.
- Their path is not guided by gravity.
- They can hit both moving and stationary targets.
- However, they consume more fuel, and generally their range will be less than Ballistic missiles.
- Example- Nirbhay missile and Brahmos missiles.
MISSILE DEVELOPMENT IN INDIA (07:43 PM)
- Integrated Guided Missile development Plan (IGMDP)
- It was envisaged by Dr. A.P.J Abdul Kalam in 1983 to help India attain self-sufficiency in the field of missile technology.
- It led to the development of 5 missile systems have been developed under this program, i.e. Prithvi, Akash, Trishul, Nag, and Agni [PATNA mnemonic].
- Prithvi- Surface to surface
- Akash- Surface to air
- Trishul- Now decommissioned and replaced With Barak missile [* Barak missile is a Quick reaction Surface-to-Air Missile ]
- Nag- these are also called fire and forget missile
- Agni- Canistered mechanism- Made of maraging steel, a canister must provide a hermetically sealed atmosphere that preserves the missile for years
-
- Hot launch and cold launch
- A canister launch system can be either a hot launch, where the missile ignites in the cell, or a cold launch, where the missile is expelled by gas produced by a gas generator that is not part of the missile itself, and then the missile ignites.
- In the case of hot launches, the problem is the heat produced by the missile at the time of launch.
-
- Cold launch is safer than hot launch as the ejection system will eject the missile by itself even if there is a missile failure.
-
BALLISTIC MISSILE DEFENCE PROGRAM (07:53 PM)
- DRDO is developing a two-tier ballistic missile defense system, that provides a multilayer shield against ballistic missile attacks.
- This Two-tier system is intended to destroy an incoming missile at a higher altitude in the exo-atmosphere and if that miscarries an endo-atmospheric will take place.
- First layer includes Prithvi Air Defence [PAD] which includes an upgraded version of Prithvi Missile Pradyumn. It will try to intercept and neutralize incoming attacks outside the atmosphere
- The second tier includes Advanced Air Defense [AAD] which will try to neutralize an incoming attack inside the atmosphere with the help of Ashwin missiles.
- [* S-400 system which India is importing from Russia is an Air defense system that can neutralize many types of targets such as missiles, and drones in the air itself. ]
The Topic for the next class- Ships and Submarines, Airpower and Emerging trend in warfare